Products
Data Encryption

myKMS provides a more convenient and professional encryption key management environment to customers from generation to destruction of encryption keys by applying the key life cycle concept based on the key management system (KMS, Key Management Systems) provided by its own product PrivacyDB.
myKMS Overview
myKMS provides
-
01
Visually convenient interface
(convenience of key management) -
02
Statistics through key data received
from KMS
(Integrated key management) -
03
Service support even in case of product
failure
(Provides uninterrupted service function) -
04
GUI manager console function support
(Encryption policy, key management) -
05
Certificate-based data access control
(IP, date, account, application, program, etc.) -
06
Encryption·decryption log record
collection/storage function
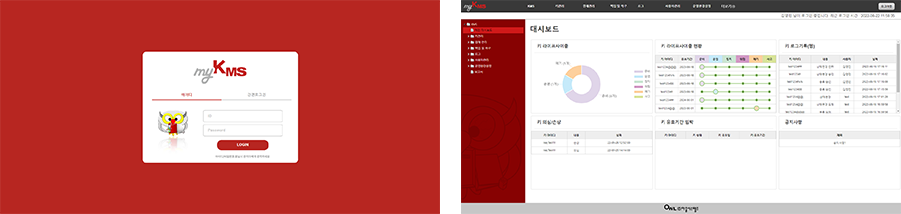
Diagram of myKMS
Main Features of myKMS
-
01
Encryption key management through encryption key lifecycle
myKMS implements and systematically manages the life cycle of encryption keys based on the NIST SP 800-57 (functions required for key management) standards referenced by the Korea Internet & Security Agency (KISA).
-
02
Web log and report function support
It performs an audit function for encryption keys by recording all work histories performed through myKMS and providing a report function.
-
03
Provides a screen that can be viewed at a glance, such as the expiration date of the encryption key, key status, and whether or not it has been damaged
You can manage encryption keys more easily and efficiently through the monitoring function that allows you to easily check various information about encryption keys on the main dashboard.
-
04
Support mobile simple authentication login function
In addition to simple ID and password input at login, simple authentication login function using mobile QR code is supported.
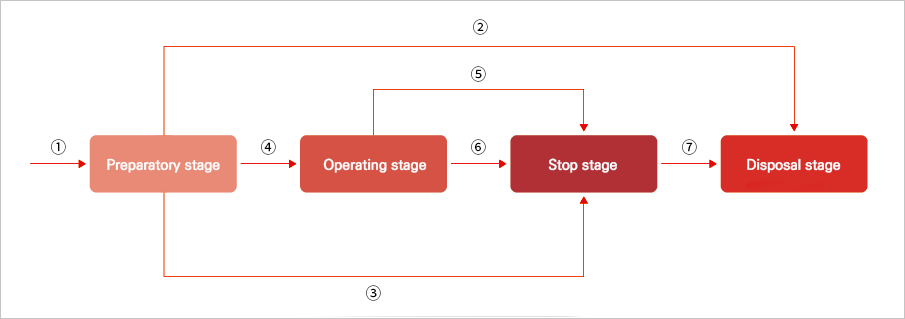
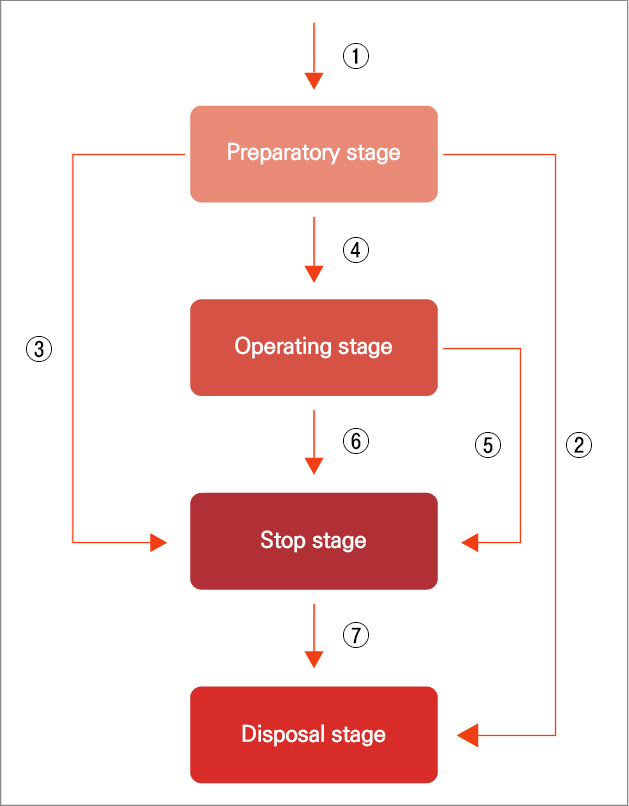
① The encryption key is in the preparatory stage as soon as it is created. (Preparation state)
② If the encryption key has been created and has never been used, the preparatory stage can be switched directly to the disposal stage and the encryption key can be destroyed.
③ If the encryption key in the preparation state gets damaged, the key administrator have to change the encryption key to the Stop stage. (Danger state)
④ Once the encryption key in the preparatory stage is ready to be used, the key administrator have to change the encryption key to the Operating stage at the appropriate time.
⑤ If the encryption key in the operating state gets damaged, the key administrator have to change the encryption key to the Stop stage. (Danger state)
⑥ If it is determined that the encryption key is not used for reasons such as expiration, but access to the encryption key is required, the key administrator have to change the encryption key to the Stop stage.
⑦ When it is clear that the encryption key in the stop stage is no longer needed, the key administrator switches the encryption
key to the disposal stage and discards the encryption key.